In industrial applications, to accurately measure temperature values, we typically use a PT100 bridge circuit to sample and convert resistance changes into voltage changes. To obtain different measurement ranges, the sampling resistors are divided into 100 ohms and 50 ohms. Method 1 and Method 2 are the measurement calculation formulas for PT100. The specific differences are as follows:
Method 1: (PT100) Reference resistor R3 = 100Ω. This method cannot measure temperatures below zero. The measurement temperature range of Method 1 is >= 0℃.
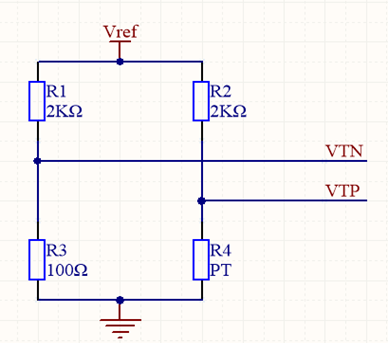
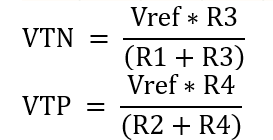
Substitute the values: R1 = R2 = 2000Ω; R3 = 100Ω; R4 = R;
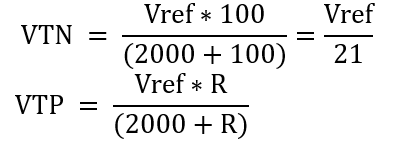
Let the measured voltage VT = VTP - VTN

as
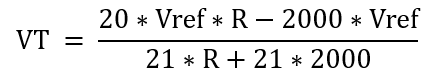
Remove the denominator,
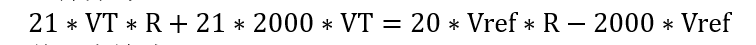
Refine expressions
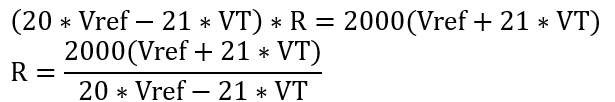
Vref is the reference voltage acquired by the AD converter, and VT is the measured voltage.
Method 2: (PT100) Reference resistor R3 = 50Ω, measuring resistance offset downwards by 50 ohms, measuring temperature range >=-125℃.
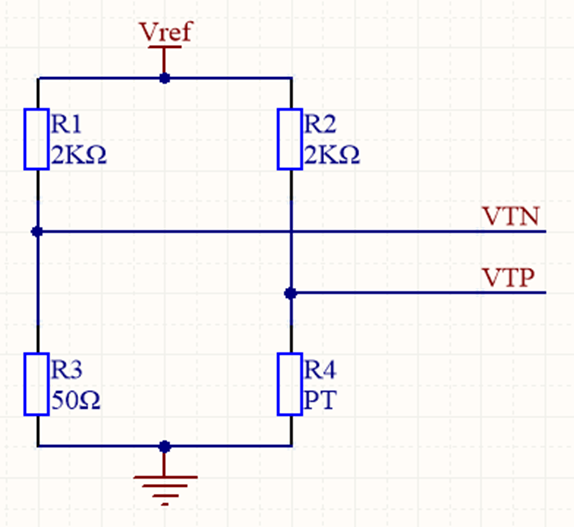
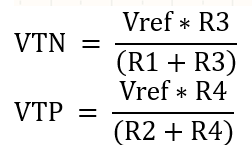
Substitute the values: R1 = R2 = 2000Ω; R3 = 50Ω; R4 = R;

Let the measured voltage VT = VTP - VTN
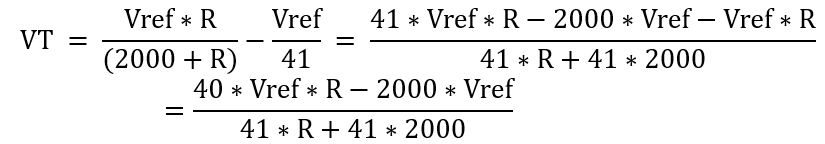
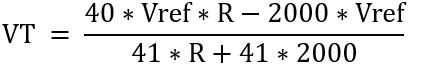
Remove the denominator,
Refine expressions
Vref is the reference voltage acquired by the AD converter, and VT is the measured voltage.
Through the calculation process above, we obtained the calculated resistance value of the PT100 by measuring the sampled voltage. To ultimately obtain the relationship between resistance and temperature, typical methods include table lookup and iterative methods.

Xml سياسة الخصوصية المدونة خريطة الموقع
حقوق النشر
@ شركة مايكرو ماجيك كل الحقوق محفوظة.
 دعم الشبكة
دعم الشبكة
