يُعد تردد الرنين لشريحة مقياس التسارع مؤشر أداء مهمًا للغاية، وهو مرتبط بنطاق تردد التشغيل الخاص بالمستشعر.
يُعدّ مستشعر التسارع نفسه بنيةً ميكانيكية، لذا فهو يمتلك ترددًا طبيعيًا. وكما هو موضح في منحنى السعة والتردد في الشكل 1، عندما يقترب تردد الاهتزاز الخارجي من تردد الرنين، يرن المستشعر، وتزداد حساسية مقياس التسارع بسرعة. والتردد المقابل في هذه الحالة هو تردد الرنين.
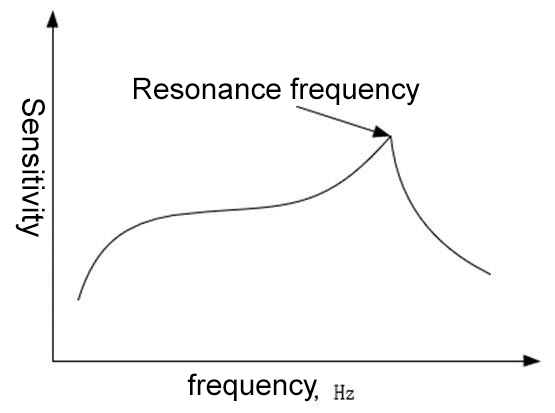
كلما صغر حجم المستشعر، ارتفع تردد الرنين. يعتمد الحد الأعلى لتردد مقياس التسارع على تردد الرنين في منحنى السعة-التردد. عمومًا، يكون نطاق تردد تشغيل مستشعر مقياس التسارع أقل من ثلث تردد رنينه. عندما يكون تردد الاهتزاز المقاس أقل بكثير من تردد الرنين، تكون إشارة خرج مقياس التسارع متناسبة مع التسارع المقاس.
كما ذُكر سابقًا، إذا زاد تردد الرنين لشريحة المستشعر، يتسع نطاق تردد التشغيل، ويصبح نطاق التردد المسطح للمستشعر أوسع، ويتسع نطاق العمل، ويمكن استخدام مقياس التسارع في سيناريوهات أكثر، وتتحسن قابليته للتطبيق. ولكن في الواقع، هناك قيود على زيادة تردد الرنين. فبحسب الصيغة التالية، كلما صغر حجم الكتلة، زاد تردد الرنين.
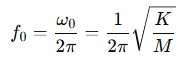
حيث f0 هو التردد الرنيني، و K هي الصلابة المكافئة لمقياس التسارع، و M هي الكتلة المكافئة للمستشعر.
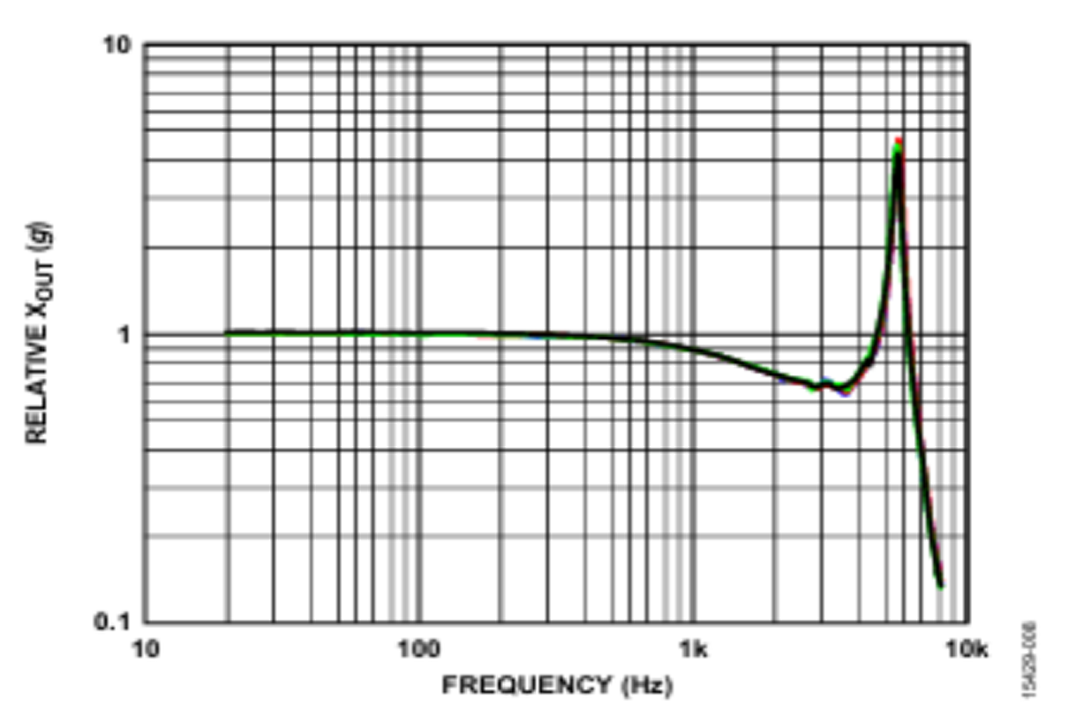
لذا، يُعدّ تردد الرنين قيدًا أساسيًا يُحدد نطاق استجابة التردد المتاح لمقياس التسارع. يتطلب التصميم والتطبيق الأمثلان أن يكون تردد التشغيل أقل من ثلث تردد الرنين، وفي التطبيقات عالية الدقة، يجب أن يكون أقل من خُمس تردد الرنين لضمان الخطية والموثوقية. يتميز استجابة التردد لمقياس التسارع ADXL356 الموضح في الشكل 2 بتردد رنين يبلغ حوالي 5.5 كيلوهرتز وعرض نطاق ترددي 3 ديسيبل يبلغ 2.5 كيلوهرتز. في التطبيقات عالية الدقة، يُضبط تردد القطع لمرشح التمرير المنخفض عادةً على أقل من 1 كيلوهرتز.

Xml سياسة الخصوصية المدونة خريطة الموقع
حقوق النشر
@ شركة مايكرو ماجيك كل الحقوق محفوظة.
 دعم الشبكة
دعم الشبكة
