يُخرج مستشعر الجهد عادةً نطاق جهد يتراوح بين 0-5 فولت أو 0-10 فولت. إذا اخترنا عدم استخدام شريحة تحويل تناظري رقمي خارجية لاعتبارات التكلفة، واستبدلناها بأخذ عينات من وحدة التحويل التناظري الرقمي داخل شريحة المتحكم الدقيق، ولكن نظرًا لأن نطاق جهد وحدة التحويل التناظري الرقمي في STM32 هو 0-3.3 فولت، فإننا نحتاج في هذه الحالة إلى دائرة أخذ العينات الموضحة في الشكل أدناه.
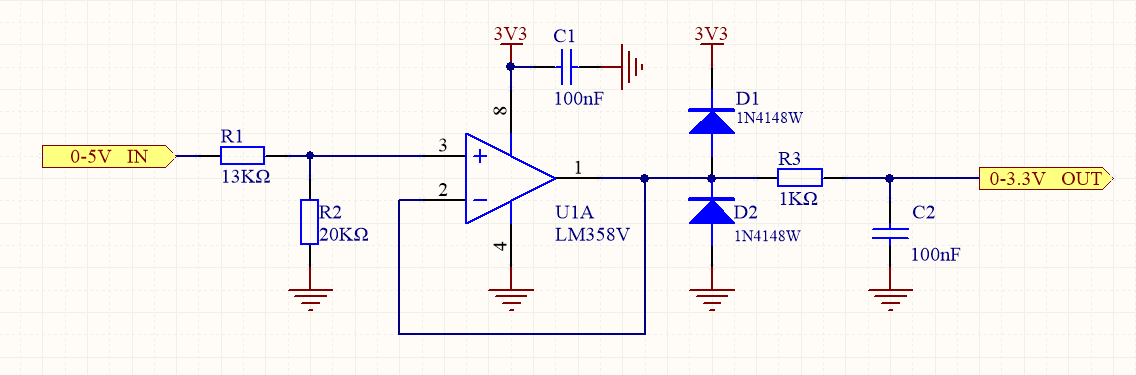
في الشكل، يشكل المقاومان R1 وR2 دائرة مقسم جهد، حيث يحولان جهد الدخل من 0 إلى 5 فولت إلى نطاق جهد يتراوح تقريبًا من 0 إلى 3 فولت. يقوم مضخم العمليات اللاحق، الذي يعمل كمتابع جهد، بمطابقة المعاوقة، وعزل المستشعر عن وحدة أخذ عينات محول الإشارة التناظرية إلى الرقمية (ADC)، وتقليل توهين الإشارة. ولمنع تلف دائرة وحدة ADC اللاحقة نتيجة الجهد الزائد أو السالب، تُضاف ثنائيات حماية من التيار الزائد إلى مصدر الطاقة والأرضي على التوالي، مما يضمن بقاء جهد دخل وحدة ADC ضمن النطاق من -0.7 فولت إلى 3.3 فولت + 0.7 فولت. في الوقت نفسه، وللحد من تأثير الضوضاء عالية التردد، يُضاف مرشح تمرير منخفض RC قبل أخذ عينات ADC. يجب اختيار تردد القطع لمرشح التمرير المنخفض وفقًا لعرض نطاق الإشارة. على سبيل المثال، إذا كان عرض نطاق الإشارة 100 هرتز، فيمكن ضبط تردد القطع على 100 هرتز أو أعلى قليلاً، مثل 1 كيلوهرتز. إذا كانت قيمة المقاومة R2 تساوي 1.5 كيلو أوم وقيمة المكثف C1 تساوي 100 نانوفاراد، فإن تردد القطع fc يساوي تقريبًا 1 كيلوهرتز.

Xml سياسة الخصوصية المدونة خريطة الموقع
حقوق النشر
@ شركة مايكرو ماجيك كل الحقوق محفوظة.
 دعم الشبكة
دعم الشبكة
